Zinc casting and iron casting parts are all common metal components in many industry fields. Depends on different applications and functionalities, These casting components can be used right places to play their performance well. Their advantages and disvantage of them, also present here significantly. For zinc casting vs. iron casting, in view of consideration of the cost, we should learn these two kinds material properties, production process and applications in detail when we need to use metal components.
With their mechanical properties, Zinc Die Casting Is Ideal for Miniature Parts Manufacturing and offer some lightweighting ratio precision components with good toughness and ductility, and eusuring lightweighting ratio components reduce the equipment overall weight. But iron casting process can create some heavy weight and big size mechanical equipment components, which are high hardness and supperior durable.

Zinc casting VS. Iron Casting Cost
| Features | Zinc Casting | Iron Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Material Cost | more expensive per kilogram, Need more higher standard composition zinc alloy | cheaper per kilogram but need higher costs in terms of machining, labor, and longer production cycles |
| Tooling and Production Costs | requires molds with high durability, suitable for high volumes. The cost of making the mold is higher.allowing quicker cycle times and reducing production costs for large volumes | Simple sand or earth mold and form iron part shapes, expense low tooling cost. High temperature iron molten need a longer cooling and solidifying, lead to high production costs. |
| Machining and Post-Processing Costs | Zinc die casting can process the precision parts with fine surface finishes, typically minimizes the need for additional machining, reducing post-processes costs. | Iron casting processes the parts with tough surface finishes and uneven areas, and requires more finishing work. May be using cnc machining to process them in further, leading to higher post-processing costs. |
| Application And Maintenece Costs | good durability, impact resistance, and is more suitable for medium-load parts. It is used for components with corrosion resistance, precision, and aesthetics. Not easy to rust, and expose in harsh and moisure air for a longer time, reduce largely the components maintenance costs during application. | require high strength and wear resistance, such as heavy-duty machinery. The iron is easy to rust if exposed in harsh environment or humidy air. These iron components should be maintained frequently, lead to a high maintenance costs during application. |
In short, Zinc Casting Compare to Iron Casting, zinc casting may be better for small sized and medium-duty, precision, or decorative parts with high production volumes. While iron casting is suitable for heavy-duty, load-bearing applications.
Zinc Casting Vs. Iron Casting Part Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties from different casting parts will decide applications and functions of the casting part. Especially zinc casting part and iron casting part, which are mostly used in different industries. Their different mechanical properties can be applied to create proper casting parts to serve various fields in many industries. the follow will mention that the difference between zinc casting part and iron casting part mechanical properties.
Zinc Casting Part Mechanical Properties
- Hardness & Wear Resistance: Main type Zamak serial alloy material, Hardness (Brinell): ~80–100 HB, Softer, easier to machine but less wear-resistant
- Impact Resistance (Toughness): Moderate impact resistance (can crack under sudden force), These zinc alloy compositon include different ratio metal elements, and need higher material composition costs.
- Fatigue Strength: Lower fatigue strength (~100–150 MPa at 10⁷ cycles). and is not suitable for cyclic loading.
- Machinability: Excellent machinability (soft, minimal tool wear), but the part is light weight, compare the duty iron part.
- Weight & Density: ~6.6 g/cm³ (lighter). zinc casting part can reduce the overall weight of the equipment and reduce energy consumption.
- Corrosion Resistance: Naturally corrosion-resistant (good for outdoor/plated parts). zinc die casting part is applied in harsh environments or moisture air.
Iron Casting Part Mechanical Properties
- Hardness & Wear Resistance: hardness:150–300 HB, Much harder, better for abrasive environments, so the iron casting part is supperior wear resistance.
- Impact Resistance (Toughness): Excellent impact resistance (similar to steel), since the iron casting part is very high hardness, and accept frequent impact each other.
- Fatigue Strength: High fatigue strength (~200–300 MPa at 10⁷ cycles). suitable for some support frame and chassis for duty industrial equipment.
- Machinability: Good machinability (graphite flakes help cutting).
- Weight & Density: ~7.1–7.3 g/cm³ (heavier), suitable for some counterweight for heavy industrial machines and reduce the machine viberation.
- Corrosion Resistance: Easy to rust, to prevent rust from surface oxide, the iron casting part can be pained, plated and coated powder.
Zinc Casting Vs. Iron Casting Precision
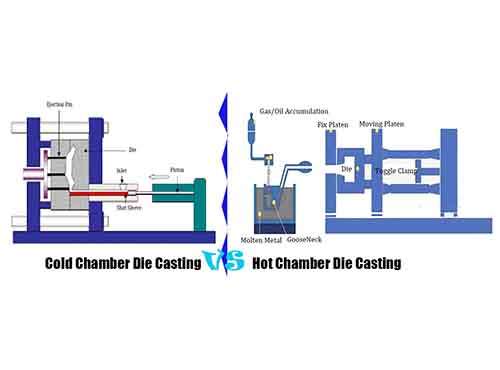
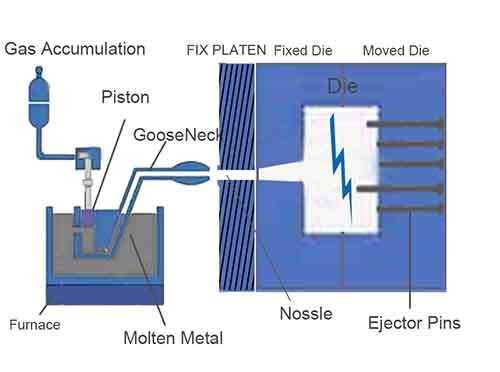
Zinc Casting processes precise metal cast parts with high precision tooling steel die, and provides supporier surface finish. In fast cycle time, the cast part can solidify quickly, even cool, and accept intricate integrated structure design and thin walled parts mass production in high efficiency. However iron casting fabricates some tough suface finish’s iron casting parts with simple sand mold, and need accepting more post- processes.
Zinc Casting Higher Precision
- With High Hardness Steel Die, Stable Molds: The steel dies are machined to extremely high tolerances. It accepts intricate structural design and supperior surface finish.
- Adopting High Pressure: The pressure ensures the molten metal completely fills the mold cavity. And create high quality integrated structural parts,and enhance production rates in mass production.
- Fast Cycle time : Exhausting less heat energy consumption, Zinc can solidify very quickly. Minimizing shrinkage and warping, which helps maintain dimensional accuracy.
- Excellent Fluidity: Molten zinc flows easily, allowing it to fill very thin walls and intricate features cavity of the die. Create fine surface finish of as-cast part.
Iron Casting Lower Precision
- Consumable Mold: The mold is made of compacted sand. On which generate uneven tough surface. It makes iron casting part surface is very tough, and need further post-processes to treat for some heavy industrial chassis and frames.
- Loose Tolerance Dimensional Demand: The sand mold is simply and toughness, and it can warp, shift, or erode during the pouring process, leading to loose tolerance dimensional variance.
- Low Pressure: Molten iron is typically poured using gravity, so uncomplete filling on the sand channels ocurred. This leads to damage the sand mold and defective cast part any time.
- Slow Cooling: Iron cools and solidifies slowly. Casting technician control and adjust iron cast part shrinkage depends on their work experience. And allow the molten iron cools naturally, and form iron cast part.
Conclusion
The above information elaberates Zinc Casting VS. Iron Casting from casting cost to mechanical properties. Zinc casting process need high precision high speed dies to produce steady dimensional cast part with small and medium sizes. These components are mostly for lightweighting equipment and reduce the overall weight of the equipment. But iron casting process is rough casting, can produce some duty industrial machines components, such as structural supporting frame and chassis. Its aim to fix heavy industrial equipment as duty counterweighter, and reduce the equipment viberation during running well.