Different raw material is processed into useful components, and used in wide range in actual life. They involve of two types of common manufacturing process, die casting and plastic injection molding processes. Through different process method, creates complex geometries and precision formed parts. Plastic injection part requires lower temperature to inject the molten plastic material and cool and solidify the intended injection parts. However die casting parts need more higher temperature to cast the molten metal material and cool and solidify casting parts. The difference between die casting and plastic injection molding is significant. These two kinds of processes play different role in industrial applications.
Die Casting
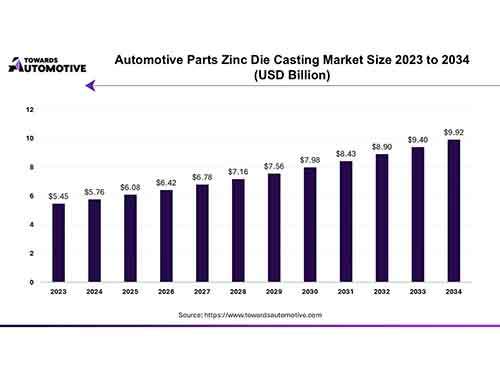
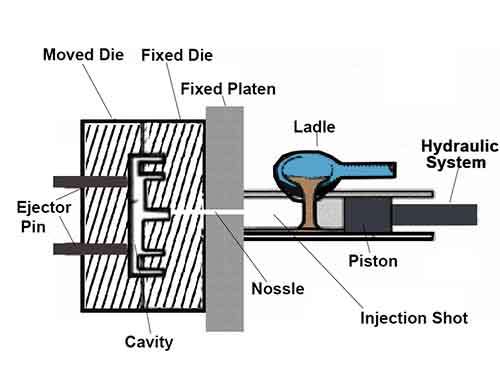
It belongs to metal die casting and solidify manufacturing process, include of two types of pocess technique, which contain cold chamber die casting and hot chamber die casting. Through precision mold, they can process hign quality metal cast parts.
Advantage Of Die Casting
- Required Raw Material: Common non-ferrous for die casting, include of Aluminum, zinc, magnesium and copper alloys.
- Process Method : Molten metal is injected under high pressure into a steel mold, Cools and solidifies the cast part.
- High Mold Cost: Select high quality steel to make metal casting die, and process the mold by high precision cnc machining. The mold runs under higher temperature,
- Fast Cast Cycle: Metal material has a faster thermal conductivity, and spent a few seconds to solidify.
- Application Industries: Automotive, Electronics, Communication, Industrial equipment component and Homehold Decorative Goods.

A Metal Die Casting Part is Ejected Out From The Die
The Metal Alloys for Die Casting
| Metal Alloys | Advantages | Common Alloy Types | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good strength-to-weight ratio, excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. | A380, A360, ADC12, A413 | Automotive parts (engine blocks, transmission cases), aerospace components, electronics housings and heat sink. |
| Zinc Alloys | High ductility, excellent surface finish, low melting point (reduces die wear), good impact strength. | Zamak 3, Zamak 5, ZA-8 | Consumer electronics, automotive components (door handles, brackets), hardware fittings. |
| Magnesium Alloys | Lightest structural metal (35% lighter than aluminum), excellent strength-to-weight ratio, good EMI shielding. | AZ91D, AM60D | Laptops/camera bodies, automotive parts (steering wheels, gearboxes), aerospace components. |
| Copper Alloys | Excellent electrical/thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, high strength. | Brass, Brozen | Electrical connectors, marine hardware, industrial machinery. |
| Lead & Tin Alloys | Low melting point, high density, corrosion resistance. | Lead, Tin Alloy | Radiation shielding, battery terminals, bearings. |
Plastic Injection Molding

The Plastic Part is Just Injected When The Plastic Injection Mold is Openend
The plastic injection molding process is common plastic forming manufacturing process. With precision high quality steel molding tools, depends on the different plastic materials, and produce consistent quality plastic injection parts.
Advantage Of Plastic Injection Molding
- Required Raw Material:Common thermoplastics or thermosets
- Process Method: Melting plastic pellets and injecting into a mold,cools the mold and forms plastic part.Longer cooling time.
- Hight Mold Cost: The plastic injection mold is processed in high precision with cnc machining equipment. Need high mold manufacturing cost.
- Slower Injection Cycle: The natural properties of plastic material conducts a slow thermal conductivity.
- Application Industries: Consumer goods, medical devices, packaging.
The Plastic Material For Plastic Injection Molding
| Plastic Material Items | Advantages | Common Material Types | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common Thermoplastics | Chemical-resistant, flexible, food-safe and fine surface finish. | Polypropylene (PP),Polyethylene (PE),Polystyrene (PS),ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) | Automotive, Packaging, Construcion and Consumer Goods. |
| Engineering Plastics | Higher Strength and Heat Resistance, wear-resistant, absorbs moisture. | Nylon,Polycarbonate (PC), POM,PET/PBT. | Automotive, Electronics, Packaging and Consumer Goods. |
| High-Performance & Specialty Plastics | high heat, chemicals, or electrical insulation | PEEK,PTFE,PPS,LCP. | Aerospace, Medical device, Electronics and Automotive parts. |
Die Casting VS. Plastic Injection Molding
Die casting vs. plastic injection molding, different material process, mold & die structure and mechanism and unique process technology. This will produce different functional parts, which are used for different applications in various industries.
| Die Casting | Plastic Injection Molding | |
|---|---|---|
| Material Processing | Using Non-ferrous, such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium, copper. | Thermoplastic, such as ABS, polypropylene, nylon. |
| Work Principle | Push the molten metal into the die uder high pressure(1,500–25,000 psi), and cool the die and solidifies and form the die casting part. | Uses a screw or plunger to inject molten plastic into the mold uder lower pressure(500–20,000 psi), cooling the mold and shape the injection plastic part. |
| Tooling & Mold | hardened steel to withstand high heat and pressure,with strong wear resistance. Include of water cooling system. | Typically made of tool steel or aluminum (for prototypes). With good polishing surface of the core, and cooling system. |
| Injection Cycle Time | Require fast injection cycle time, avoid long cooling time lead to warpping and deformed. | Spend natural time to cool and form, under natural pressure and fill the plastic mold. |