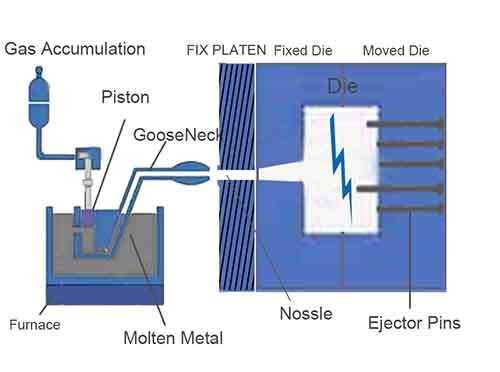
There are Two types of zinc alloys in zinc die casting process, they are Zamak and ZA alloys. As the most common zinc alloys- zamak,are used widely than ZA in zinc die casting. Depends on its several significant advantages, most of zinc die casting components are made of zamak alloys in modern industrial manufacturing process. This is due to zamak’s castability, good molten fluidity, lower melting temperature and fine metal mechanical properties. But ZA alloys are adopted for some special functions and applications in some special fields.
What Are The Zamak Alloys ?

Zamak alloys are a family of serial products on basic of zinc alloys. As the most common zinc alloys- zamak, are basic of zin element composed with other metals to improve its properties, such as strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Certainly they are mixed with zin in zinc alloys include aluminum, copper, magnesium, dIfferent other metal elements cotents, result in differeent alloys properties. Zinc Die manufacturer select the approporiate zamak alloy to process the die casting components depends on the requirement of functionalities and applications of the cast part. For example, you can choose the Zamak 3 when the client needs the miniature electric component with thin wall because of zamak 3 has a good ductility and ensure fine thin wall.
Compositions of Zamak Alloys
| Alloy | Zinc (Zn) | Aluminum (Al) | Magnesium (Mg) | Copper (Cu) | Key Characters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zamak 2 | ~95% | 3.8–4.2% | 0.02–0.05% | 2.7–3.3% | High hardness, easy maching and Good toughness |
| Zamak 3 | ~95% | 3.8–4.2% | 0.02–0.05% | <0.10% | Most common, ease castable and good corrosion |
| Zamak 5 | ~95% | 3.8–4.2% | 0.03–0.08% | 0.7–1.1% | Improved strength and corrosion resistance. |
| Zamak 7 | ~95% | 3.8–4.2% | 0.005–0.02% | <0.10% | High purity, good fluidity and better for plating. |
Zamak Alloys Applications
Zamak 2 : The strongest Zamak alloy but less ductile due to high copper content. It is used for precision mechanical parts requiring wear resistance.
Zamak 3 : The most widely used alloy has excellent castability, smooth surface finish, and good mechanical properties. It is made into automotive parts (door handles, emblems), hardware, consumer electronics and toys.
Zamak 5 : Similar to Zamak 3 but with higher strength and hardness than Zamak 3. It is used for high-stress parts like gears, locks, and industrial components.
Zamak 7 : A high-purity version of Zamak 3, and with good fluidity, better being plated. It is applied for decorative fixtures, bathroom fittings, jewelry.
What Are ZA Alloys ?

ZA alloys are another serial products among zinc family on basic of zinc alloys. So this kind of zinc alloys are often used in applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. ZA alloys are lighter than zamk alloys due to higher aluminum content composition. This kind of alloy metal always has a strong tentile strength, and ensure the die casting part has a good integrated structure. So ZA alloys are applied for many lightweight precision components for aersopace and automotive industries. But ZA alloys all have a higher melting points (420-480°C), comparison to one of Zamak alloys(380-420°C).
Composition Of ZA Alloys
| Alloy | Zinc (Zn) | Aluminum (Al) | Copper (Cu) | Magnesium (Mg) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZA-8 | ~91% | 8.0–8.8% | 0.8–1.3% | 0.015–0.03% | Castable & strong strength. |
| ZA-12 | ~87% | 10.5–11.5% | 0.5–1.2% | 0.015–0.03% | Stronger than ZA-8, ease castable, hight weight ratio |
| ZA-27 | ~70% | 25.0–28.0% | 2.0–2.5% | 0.01–0.02% | High lightweight, strong wear resistance, used in bearing and industrial parts |
Zamak Alloys Applications
ZA-8: Best for die casting among ZA alloys, And has a lowest melting points, It is used for automotive components, small gears, and electric components housings.
ZA-12 : Stronger than ZA-8, but less commonly die-cast, with good wear resistance and load-bearing capacity. It is applied for bushings, bearings, and industrial machinery parts.
ZA-27 : Poor castability in die casting, excellent bearing properties (low friction, high wear resistance). It is used for heavy-duty bearings, gears, and structural components.
Zinc Alloys-Zamak,Are Used More Wider Than ZA
Zinc Alloy-Zamak can be used more wider than ZA due to lower cost and high efficiency mass production. Proven through practice that zamak alloys have better fluidity and ducility, and more harder than ZA. So zamak can be used in various industries, how ZA is only for some specific fields, which require lightweight applications.
Zamak Vs. ZA Alloys
Zamak Alloys melting points is always lower than ZA Alloys ones, and also a better castibility. From other metal metal elements on basic of zin metal, different other metal content composed with zin metal, and result in variant zinc alloys.
| Property | Zamak Alloys (2, 3, 5) | ZA Alloys (8, 12, 27) |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Content | Low (~4%) | High (8-27%) |
| Copper Content | Low to moderate (0-3%), lower hardness, | Low to moderate (0.5-2.5%), higher hardness and wear resistance, |
| Strength | Moderate | Higher (especially ZA-27) |
| Hardness | Lower | Higher |
| Melting Point | Lower (380°C-420) | Higher (410-480°C) |
| Fluidity (Castability) | Excellent | Good (but less than Zamak) |
| Wear Resistance | Lower wear resistance | High wear resistance due to higher Al |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Better (higher Al improves corrosion resistance) |
| Cost | Lower process cost, minimal post-process | Higher process cost due to more Al content |