These two types of die casting are common processes in modern industrial manufacturing. Cold chamber die casting is ideal for higher melting point metal, such as aluminum, iron, copper and stainless steel alloys. However hot chamber die casting fits lower melting point metal, such as zinc, magnesium, lead and tin alloys. These two main industrial manufacturing processes meets the requirements of applications in most industries. Depends on the specific demands of die casting parts, die casting manufacturer choose the right die casting process technology to produce the casting parts in high effective. Today, let us to discuss the hot topic “cold chamber vs hot chamber die casting” in detail though the below aspects.
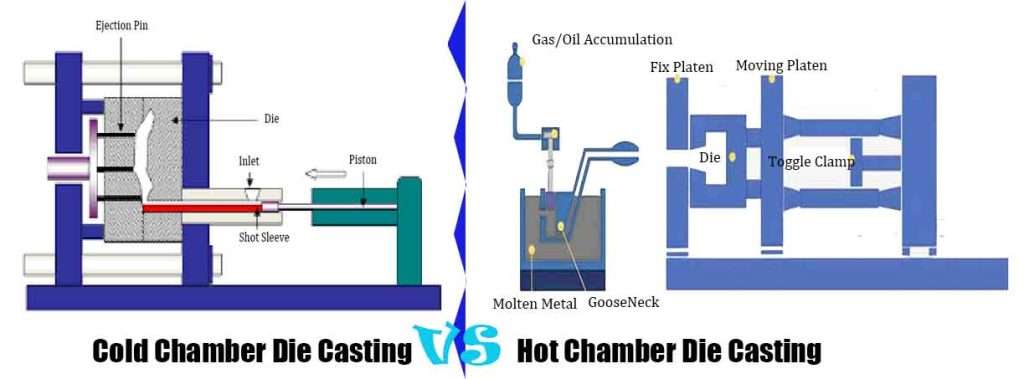
Understanding Cold Chamber Die Casting
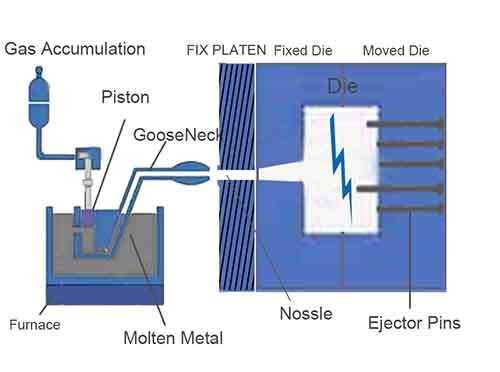
What Is Cold Chamber Die Casting ?
Cold chamber die casting is a process in which the melton metal furnace is seperated from the machine completely, and require ladling the molten metal and feeding it into the shot and pushing the molten metal into the die with hydraulic piston and fill the die fully under high pressure, cooled and solidified and form as-cast part. These higher melting points metal, such as aluminum, copper, stainless steel alloys.
Suitable Die Casting Materials
| Metal Alloy Items | Material Examples | Characters |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | A380, A360 and ADC12 | Lightweight, Excellent corrosion resistance and high thermal & electrical conductivity |
| Copper Alloys | Brass and Bronze | Excellent thermal & electrical conductivity, High corrosion resistance and high hardness |
| Iron | Iron | High density, Strong corrosion resistance and Durability |
| Stainless Steel | SUS 201, SUS202, SUS 402, SUS 403 | High hardness, excelent surface finish and high corrosion resistance |
Advantages Of Cold Chamber Die Casting
- Suitable for higher melting point metal alloys, such as aluminum, iron, copper and stainless steel alloys.
- Equipped with specific melting furnace and overflow impurity
- Ladling the molten metal from separated molten pool and inject it into the die.
- Lower cooling and solidifying but forming fine surface finish as-cast part.
- Slower cast cycle and timely die & mold maintenance
- Cost-effective mass production
- Complex geometries design and strength structural steady
- Tight tolerance dimension process
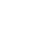
Overview Of Hot Chamber Die Casting
What Is Hot Chamber Die Casting ?
In the die casting, molten furnace is integrated with the machine. Feeding the metal material into pow, and melting metal material and overflow impurities and keep purified and steady temperature molten matail for injection. Though gooseneck mechanism, The hydraulic piston pushes the molten metal into the preheated die. Then under high pressure the molten metal flow fills into the die fully, cooled and solidified, the die is opened, the desired cast part is ejected out of the die. So hot chamber die casting is ideal for low melting point metal, such as zinc, lead and tin alloys. Hot Chamber Die Casting Is The Key Technique For Zinc Alloys Casting.
Suitable Die Casting Material
| Metal Alloy Items | Material Examples | Characters |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc Alloys | Zamak 3, Zamak 5 ZA-8 | Excellent dimensional stability, High ductility & impact resistance and easy to cast |
| Magnesium Alloys | AZ91D, AM60B, AE44 | Extremely lightweight (~35% lighter than aluminum), Good stiffness & damping properties and excellent machinability |
| Lead Alloys | Lead | Very low melting point, high density, and soft, easy to cast |
| Tin Alloys | Tin | Very lowe melting point, under 200 degree, |
Advantages Of Hot Chamber Die Casting
- Suitable for lower melting point metal alloys, such as zinc, magnesium, lead and tin alloys.
- Built- in molten furnace and overflow impurity
- Gooseneck mechanism and maintain fast molten metal injection
- Fast cooling and solidifying and forming fine surface finish as-cast part
- Fast cast cycle and longer die life
- Cost-effective mass production
- Tight tolerance dimension process
Cold Chamber VS Hot Chamber Die Casting
From the below table comparison between the two type die casting process, we can find that there are their own features. This also let us to have a clear understanding between cold chamber and hot chambe die casting processes.
| Feature | Cold Chamber Die Casting | Hot Chamber Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Process Mechanism | Molten metal is ladled into a die and inject cast part. | Metal alloy is melted in an integrated furnace and injected directly and form the cast part. |
| Suitable Metals | High-melting-point alloys, such as aluminum, brass, copper, magnesium, lead and tin alloys. | Low-melting-point alloys (Zinc, Lead, Tin, some Magnesium). |
| Injection Pressure Required | Higher pressure (up to 200 MPa). | Lower pressure (typically 7–35 MPa). |
| Cycle Speed | Slower, requires manual ladling operation, and feed the molten metal into the inlet and start casting. | Faster, inject the molten metal into the die directly. |
| Die Life | Longer die life due to lower temperature and low wear consumption. | Shorter die life due to higher temperature wear |
| Production Volume | Medium to large batches. | High-volume production. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher melting metal cost, and slower cast cycle | Lower mass production cost. |
| Geometry Sizes | Medium and large size die casting parts | Miniature die casting parts, accept complex geometries design |
| Porosity & Strength | Less porosity, stronger parts due to high pressure. | Good surface finish but slightly more porous. |
| Applications | Automotive (engine parts), aerospace, industrial. most used for lightweight applications | Electronics, small components, |