TangSheng Hardware Technology, as one of professional die casting manufacturers, mainly offter two types of metal die casting parts, include of zinc alloys and aluminum alloys die casting processes. The die casting parts that we produce used for automotive, communication, medical and consumer electrics industries. We have been learned more about zinc and aluminum alloys properties, and choose best composition alloy for functions and applications of part, provided high precision metal die casting parts across many industries. These common aluminum and zinc alloys can be processed into high precison parts by different casting technique respectively. They are Hot chamber die casting and Cold chamber die casting processes. we will observe the benefits applicable to each alloy.
Aluminum Alloys for High-Precision Casting
Common Aluminum Alloys Items Run At TangSheng
| Alloy | Composition | Properties | Applicatons |
|---|---|---|---|
| A380 | ~8.5% Si, 3.5% Cu, <1% Fe, <3% Zn | Excellent fluidity, good strength, and pressure tightness | Engine brackets, gearboxes, electronic housings |
| A383 | ~10-12% Si, 2-3% Cu | Improved die-casting performance, reduced hot cracking | Thin-walled components, automotive parts |
| A360 | ~9-10% Si, 0.4-0.6% Mg | Superior corrosion resistance, good pressure tightness | Marine components, hydraulic systems |
| A413 | ~11-13% Si | Excellent castability, high impact resistance | Complex thin-walled parts, optical mounts |
| AlSi7Mg (A356, A357 – T6 heat-treated) | ~7% Si, 0.3% Mg | High strength, good weldability, and machinability | Aerospace, high-stress structural components |
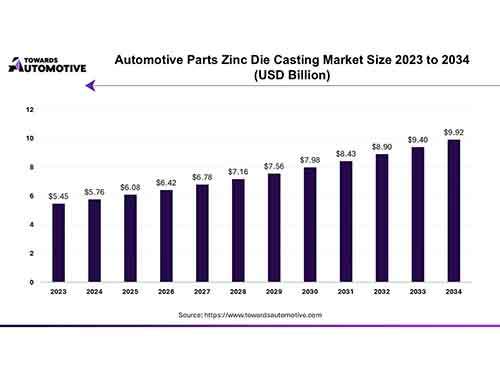
Cold Chamber Die Casting
Cold chamber die casting is a process in which the melton metal furnace is seperated from the machine completely, and require ladling the molten metal and feeding it into the shot and pushing the molten metal into the die with hydraulic piston and fill the die fully under high pressure, cooled and solidified and form as-cast part. These higher melting points metal, such as aluminum, copper, stainless steel alloys.
Zinc Alloys for High-Precision Casting
Common Zinc Alloys Items Run At TangSheng
| Alloy | Composition | Properties | Applicatons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zamak 3 | ~4% Al, 0.03% Mg, <0.1% Cu | Best balance of strength and ductility, excellent castability | Gears, connectors, consumer electronics |
| Zamak 5 | ~4% Al, 1% Cu, 0.03% Mg | Higher strength and hardness than Zamak 3 | Automotive components, precision hardware |
| Zamak 7 | ~4% Al, 0.005% Mg, <0.1% Cu | Improved corrosion resistance, minimal intergranular corrosion | Medical devices, outdoor equipment |
| Zamak 8 | ~8.4% Al, 1% Cu, 0.02% Mg | High strength, good wear resistance | Bearings, bushings, high-load parts |
| ACuZinc (Zn-Al-Cu-Si) | ~5% Al, 2.5% Cu, <1% Si | Superior creep resistance, high-temperature stability | Die-cast automotive parts, industrial fittings |
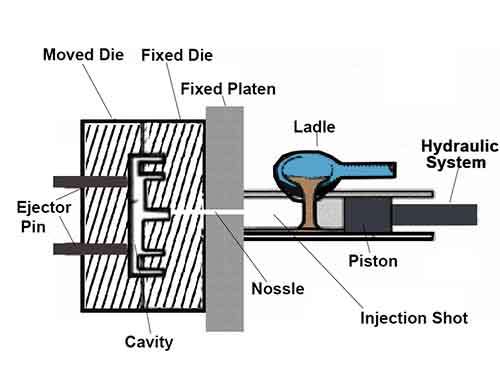
Hot Chamber Die Casting
In the die casting, molten furnace is integrated with the machine. Feeding the metal material into pow, and melting metal material and overflow impurities and keep purified and steady temperature molten matail for injection. Though gooseneck mechanism, The hydraulic piston pushes the molten metal into the preheated die. Then under high pressure the molten metal flow fills into the die fully, cooled and solidified, the die opens, the desired cast part is ejected out of the die. So hot chamber die casting is ideal for low melting point metal, such as zinc, lead and tin alloys. Hot Chamber Die Casting Is The Key Technique For Zinc Alloys Casting.
Aluminum Alloys Vs. Zinc Alloys
Aluminum Alloys Pros And Cons
The aluminum alloys are one type of common metal alloys, they have their own pros and cons, we observe the below chracter.
Advantages Of Aluminum Alloys
- Lightweight
- Good Strength-to-Weight Ratio
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance
- High Machinability
- Good Thermal & Electrical Conductivity
- Castability & Fluidity
- Recyclability
Disadvantages Of Aluminum Alloys
- Lower Hardness & Wear Resistance
- Higher Cost Than Zinc Alloys
- Lower Dimensional Stability
- Porosity in Castings
- Surface Finishing Challenges

Aluminum Alloy Die Casting Parts , very light weight, its surface finishes are diversity. Easy surface finishes are anodized, painting, powder coated. But electroplating is very difficult due to aluminum alloy properties, and belong to porosity metal, more pretreating processes for electroplating.

Zinc Alloy Die Casting Parts, belong to high precision metal components , and used for a wide range, from automotive to communication industries. The casting parts have a steady dimensions and good strength integrated structure, with strong corrosion resistance.
Zinc Alloys Pros And Cons
Advantages Of Zinc Alloys
- Superior Castability & Fluidity
- Excellent Dimensional Stability: Low shrinkage
- High Strength & Hardness
- Smooth As-Cast Surface Finish
- Faster Production Cycles
- Cost-Effective for Small, Complex Parts
Disadvantages Of Zinc Alloys
- Heavy: 2.5x denser than aluminum
- Limited High-Temperature Performance
- Corrosion Resistance Requires Plating
- Brittleness in Certain Alloys
- Not Ideal for Large Parts: