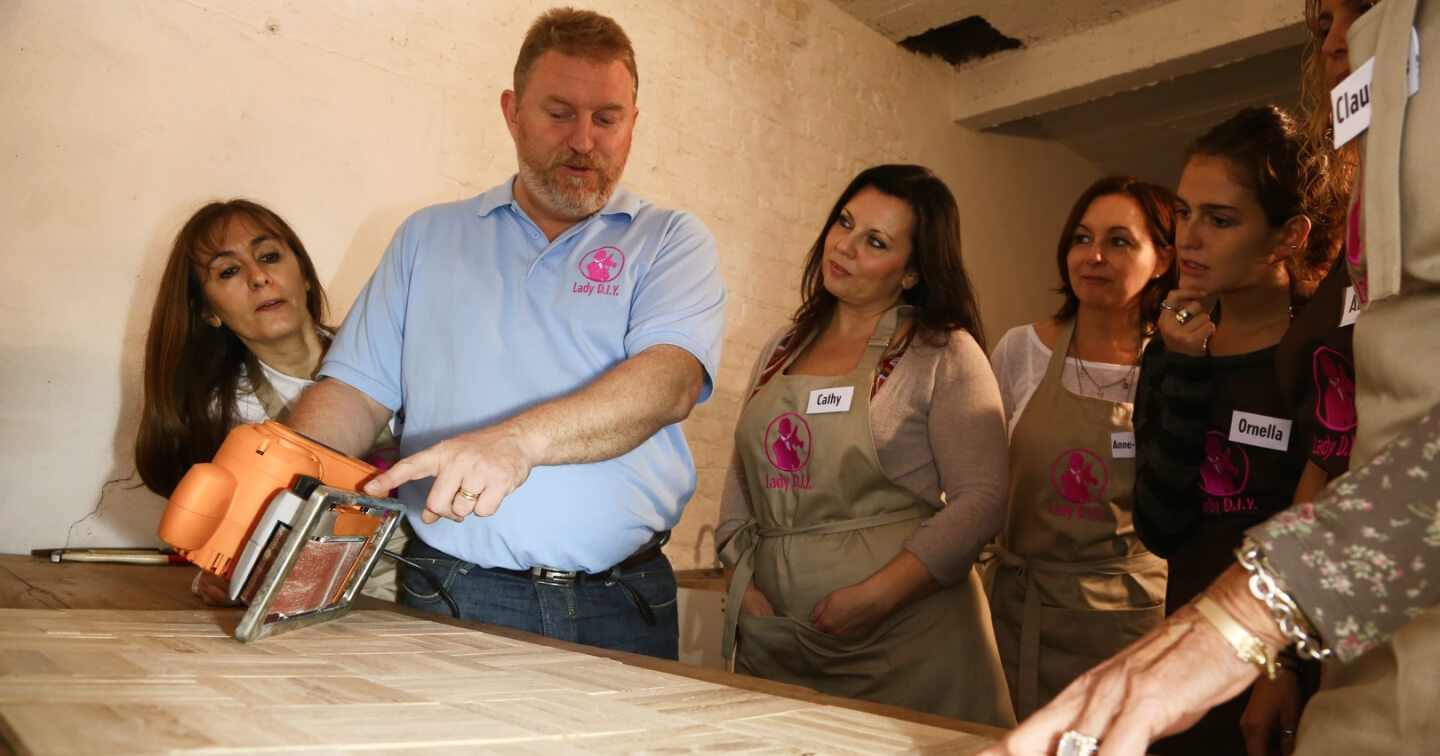
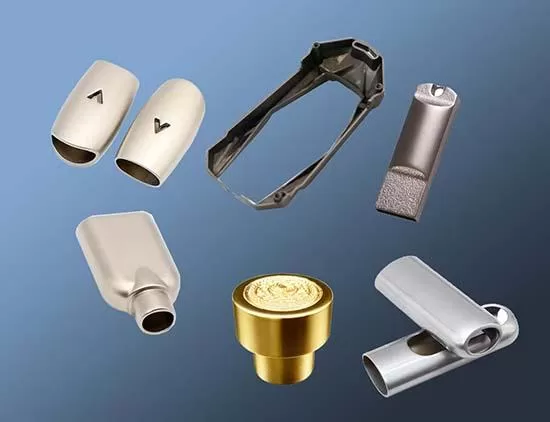
With the rise of newly indutries, More miniature and precision components are required to meeting the demand of these industry development. More and more die casting manufacturers begin to engage in production of various metal die casting components which involves copper die casting, stainless steel die casting, iron die casting and zinc die castng. They found that most widest applications die casting are aluminum and zinc die casting process. However, zinc die casting process for zinc alloys is most common in metal die casting process, which offers high effective mass production and mininal material waste, and follows environmental management standard. What is The Most Common Casting Process for Zinc Alloys? That is hot chamber die casting process.
Understand Hot Chamber Die Casting Process
What is Hot chamber Die Casting Process ?
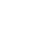
Hot chamber die casting process is unique metal die casting process method, which is suitable for zinc, lead, tin, and magnesium alloys manufacturing process. It enables providing high efficiency mass production at fast casting cycle for small and medium sizes precision components. Using integrated furnace with die casting machine, store preheated molten material inside, through special gooseneck mechanism, drive the molten material into the die directly, and formed and cooled , eject the shaped casting part out from the die.
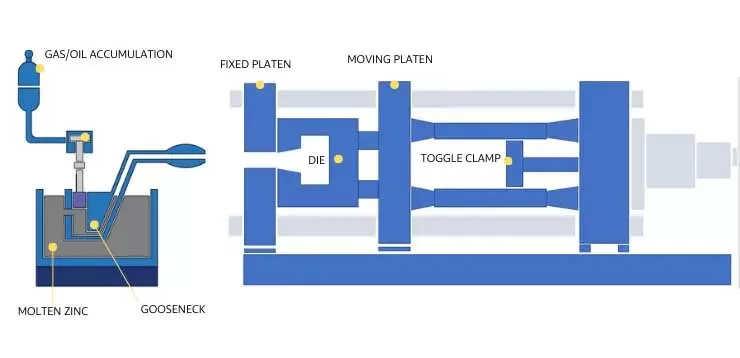
Step-by-Step Process Guideline
Advantges Of Casting Zinc Alloy With Hot chamber Die Casting Machines
In industrial manufacturing, zinc die casting parts are produced with hot chamber die casting manchines by die casting manufacturers. With The Technique Of Supporting Casting Zinc Alloy With Hot chamber Die Casting Machines consistent optimization, manufacturers can produce high quality zinc die casting components under its unique technique. In another one, zinc good fluidity in molten status makes it forming smoother surface finish. The fine suface finish reduce the work volume of post-process. It advantages reflects the below detailed descriptions.
1.Fast Speed Cast Cycle
The low melting points metal can cool quickly and solidify and ejected out from the mold, saving cooling time. reduce overall production cycle time. Hot chamber machines are designed for quick setup and operation, making them ideal for mass production. Hot chamber machines have a high efficiency production speed and guarantee of high quality for processing products.
2. Shape Intricated Precision Geometies
Zinc alloys have excellent flow characteristics. Can shape intricated geometries and thin-walled parts can be cast with precision. Fully fill the cavities of the casting die under high pressure, generates less defects and imperfections, and reduce waste material in mass production. Zinc alloys cast using hot chamber machines can produce superior dimensional accuracy parts and Shape smoother surface finish. It is call as “As-Cast Finish” which may have a precision dimension and tight tolerance precision.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
The precise injection process minimizes wastage and ensures more consistent parts. Zinc low melting points can also save more energy cost. The hot chamber die casting process have a greater cost-effectiveness.
4. Improved Surface Quality
With Precision casting die, using hot chamber die casting process , lead to excellent surface finishes that often require minimal post-processing. This dues to a good fluidity of zin metal and precision casting dies.
5. Longer Die Life
Zinc’s low melting points reduces thermal wear on dies, prolonging casting die lifespan and reducing tooling costs. meanwhile reduce Zinc Casting Die Maintenance and Repair times.
Conclusion
In Summary, the Most Common Casting Process for Zinc Alloys is Hot Chamber Die Casting Process. From the principle of the process, it simplifies process steps, also beneficial to inject the molten metal. Using integrated furnace to melt zinc alloy and store preheated metal molten in the reservior and oveflow the impurities inside molten material. The piston drive the molten material from integrated reservior to the cores and cavities of the die directly through the gooseneck mechanism. Then cools and solidfies the shaped part. The process is suitable for zinc, lead, tin, and magnesium alloys manufacturing process. Because these low melting point metal can provide high precision, flexible design, small and medium sizes components. Additionally, these low melting point metal needs cost-efficiency mass production.