When we need producing zinc die casting components to meet the demands of some specifications in many fields, firstly we will consider that a Zinc Die Casting Components Design Guide is indispensable. Complying with the guideline, Our engineers can create high effective, cost-effective, and reliable zinc die-cast parts. Here is step-by-step zinc die casting component design guide to design good quality zinc die casting components to meet the demands of many fields.
Read the content step by step
- Zinc die casting component design guide
- Professional Engineering Design Team Offers High Quality Zinc Die Casting Part Design Service
- Conclusion
Zinc Die Casting Component Design Guide
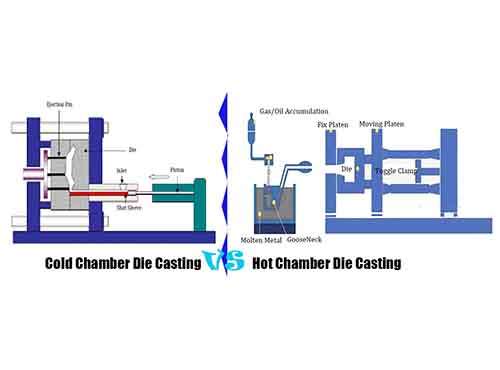
Zinc die casting component design should follow hot chamber die casting, which provide high precision, small and medium size metal castings in high volume production under fast cast cycle. By Hot Chamber Die Casting Machine Produces High Quality Zinc Casting Parts .These small casting parts design will comply with the below steps to proceed.
No.1 Material Selection for Zinc Die Casting
Understand any specific requirements, including cast part structural, aesthetic, or functions. Choose the zinc alloy that best suits the component’s function and applications. Hereby we focus on the most common zinc alloys, Zamak alloys, which have their own properties respectively. The common several types of them are listed as the follow.
Zamak Serial
| Zinc Alloys | Composition | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Hardness (Brinell) | Impact Strength | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zamak 2 | ~95.5%,Zn,3.5-4.3%,Al, 2.5–3.5%,Cu, 0.02–0.06%, Mg, Other,<0.1 Fe, <0.007 Pb | 328–359 | 208–240 | 7-10 | 82-100 | 53–58 | High-wear parts (gears, bushings). |
| Zamak 3 | ~95.5%,Zn,3.5-4.3%,Al, 2.5–3.5%,Cu, <0.1%, Mg | 283–328 | 208–240 | 10–15 | 80–90 | 48–53 | Consumer electronics, decorative hardware. |
| Zamak 5 | ~95.5%,Zn,3.5-4.3%,Al, 2.5–3.5%,Cu, 0.75–1.25%, Mg, | 317–359 | 228–262 | 7–10 | 91–100 | 41–48 | Automotive (locks, carburetors). |
ZA(Zin-Aluminum Alloys)Serial
| Zinc Alloys | Composition | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation Content | Hardness (Brinell) | Impact Strength | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZA-8 | ~91.1%,Zn,8.0-8.8%,Al, 0.8–1.3%,Cu, 0.015–0.03.3%, Mg, | 374–386 | 283–317 | 6-10% | 100–110 | 35–41 | Small precision parts (connectors) |
| ZA-12 | ~86.5%,Zn,10.5-11.5%,Al, 0.5–1.2%,Cu, 0.015–0.03%, Mg, | 400–414 | 317–345 | 3-6 | 110-120 | 25-30 | Industrial components (gears, housings) |
| ZA-27 | ~70%,Zn,25-28%,Al, 2.0–2.5%,Cu, 0.01–0.02%, Mg, | 400–440 | 345–386 | 1-3 | 115-130 | 15-20 | High-strength applications (aerospace) |
Depends on the function requirements of the cast part, we should choose the best zinc alloy to cast component.

No.2 Consider Zinc Die Casting Component Design Constraints
- Wall Thickness : Design uniform wall thickness between 0.5mm to 5mm throughout the component to minimize defects and ensure structural integrity.
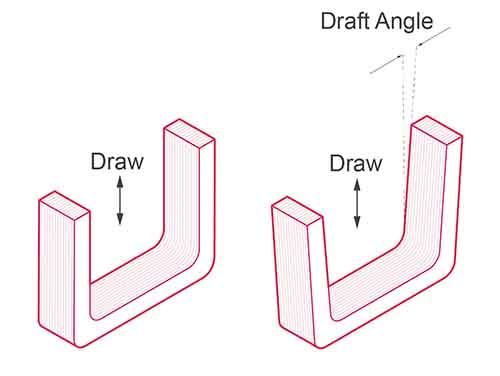
- Draft Angles : Keep all vertical walls having a draft angle between 1° and 3°. This helps ejecting out of the part from the die.
- Undercuts: Slides/Lifters can be used but add cost if possible. But the fuction can resolve the design of intricate structure and functionalities of the cast part.
- Fillet Radii: Stress concentrators → use radii (R ≥ 0.5 mm), minimum 0.3 mm radius to improve flow & reduce cracking.
- Parting Line & Ejection: Parting Line Location: Should minimize flash & finishing work, Ejection Pins: Design to avoid visible marks on critical surfaces.
- Ribs & Bosses: To reinforce the structural integrity of the part, add ribs without significantly increasing weight or material costs. Bosses designed is convenient to assemble and avoid thick sections that can cause shrinkage.
- Surface Finish & Textures: Polished Molds can achieve smoother finishes, texture treatment needs some precision process equipment to process .
- Post-Casting Considerations: Flash removal, deburring, further machined by cnc machining and various coating of die castings.
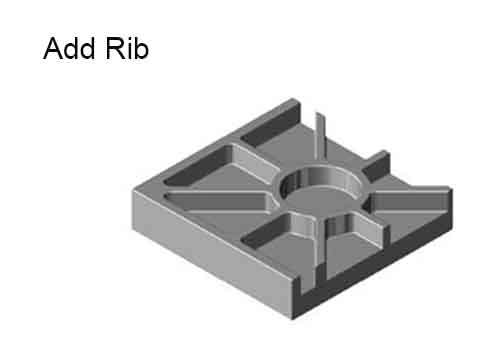
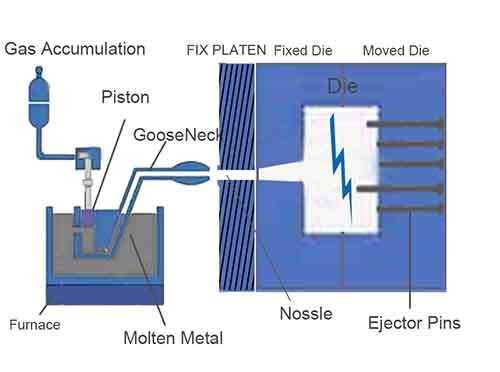
No. 3 Optimization for Detail Design and The Die Improvement
Our engineers can access the aesthetic and functional needs of the die casting part, position the part line location and minimize impacting the part appearance. Place ejection pins in non-visible or non-functional areas to avoid marks on critical surfaces. Meanwhile control ejection pin push power avoid over push power to deform the part. Optimizing these optimal gates and vents to ensure efficient material flow and minimal air entrapment. and ensure the as-cast part high qulity.

No.4 Rapid Prototyping and Testing
Create a prototype to test functionality, fit, and performance before mass production in shorter time. Prototypes can be produced by precision casting die, If neccessary we can engage in further post-process like CNC machining, grinding, polishing or coating treatments to realize the functionalities of the cast part. Then begin to test its assembly and fit other components smoothly and identify its performance. The first samples testing should be addressed before moving to high volume quantity production.

No. 5 Final Design Adjustments
Engineer can adjustments based on testing results, improve design aspects like wall thickness, rib locations, or gate and vent places, until the qualified prototype is confirmed. Once the design is validated, finalize the die design and manufacturing parameters. Record these test result and part parameters, include of the part material, cast cycle time, cooling and solidification temperature and the pluger force power.

By the above these steps, we can produce zinc die casting components in large scale in cost-effective. And suited to various applications. Zinc Die Casting Components Design Guide is execution documents before making samples for mass production. In another one, it need designer to consider to simulition software to simulite running casting die process to check some predicted defects and trouble during making samples.
High Quality And Fast Lead Time
Expertised Engineering Team And Well-experienced Die Casting Manufacturing Technique Offter Satisfied Services
Tscasting Technology Offer High Quality Zinc Die Casting Component Design Service
As one of professional zinc die casting manufacturers, We have a professional engineering design team that provides strong technical support is a major asset in zinc die casting. This team can work closely with clients to optimize component designs for manufacturability, troubleshoot technical issues, and incorporate client-specific requirements. We offer high quality zinc die casting part design service. and down the following ability.

Various Zinc Alloy Composition Casting Technology
We have a deep understanding of zinc alloys, including Zamak and ZA series alloys, and their specific properties and applications. And Ability to select the best zinc alloy for each application, balancing performance, cost, and environmental considerations.
Advanced Design and Simulation Skills
Our engineering team can use advanced CAD software to create precise, manufacturable designs. Using casting simulation tools to predict and resolve potential issues (e.g., air entrapment, shrinkage, material flow) before production. We also consider of die casting constraints involves of integrate features like draft angles, uniform wall thickness, and fillets, optimization for the die casting process.
Die Design and Optimization
Our ability to design dies that ensure efficient, high-quality production. including optimal gating, venting, and cooling systems. Expertise in die maintenance practices to extend die life and maintain product quality. The precision die should be optimized and improved after Prototype and Testing,and ensure enhancing the wear resisitance and the life span of the mold.
Problem Solving and Troubleshooting
Skilled in optimizing cycle times, material flow and retain a good melting material fluidity. Ensure the casting part has a uniform cooling. Ability to quickly identify and resolve issues, such as porosity or warping, ensuring consistent product quality.
Customization and Flexibility
We collaborate closely with clients, incorporating specific requirements and providing tailored solutions. especially the design of custom die casting parts. Flexiblely designing components for a variety of industries, such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods, meeting unique standards and specifications.
Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Ongoing research into new zinc alloys, coatings, or manufacturing technologies to stay competitive and offer advanced solutions to our clients. Being familiar with lean principles to reduce waste, optimize processes, and improve cost-efficiency.
Conclusion
In summary, A sound zinc die casting component design guide should be made before proceeding design a zinc custom die casting part. we can have a concise summary for designing zinc die casting components. As guidance for design high quality zinc die casting part, which can guide us to select the best zinc alloy, Consider Die Casting Constraints, Optimization for Manufacturing and Efficiency, Prototype and Testing and design modification and adjustion, until produce high quality zinc die casting components.