ZA(Zinc-Aluminum) Alloys and Zamak alloys blong to two kinds of zinc alloys in one of family of zinc, Depends on their composition, metal properties, These zinc alloys will be used for casting desired zinc die castings to meet the versitile requirement in different industries. ZA alloys contain higher aluminum content, higher melting points, which are used for components for lightweight, excellent mechanical properities and high strength. However Zamak alloys are common zinc alloys, which contain lower aluminum content, but harder, lower melting points, which are used for some common consumer electronics, gifts and hardwares. So they also have their different application respectively. Now ZA Alloys vs. Zamak Alloys, and different Applications, From the follow key points, look in their difference and benefits in depth.

ZA Alloys Vs. Zamak Alloys Material Composition
Different composition content decides different metal properties. Zin-aluminum alloy(called as ZA) contain higher aluminum content, and requires higher temperature to melt the metal, comparison to common zamak alloy, which blong to lower melting points metal. So ZA is lower than Zamak in density. ZA Alloys vs. Zamak Alloys Material Composition as the below.
ZA Alloys Material Composition
Zn (~80-90%), Al (~8-28%), Cu (~1-3%), Mg (~0.01-0.03%), Higher aluminum content,Hardness: 90-120 BHN, Higher Impact Resistance, Excellent Wear Resistance, Melting Point: 375-485°C. More expensive but offer superior strength. Common ZA alloys include of ZA-8, ZA-12 and ZA-27
Zamak Alloys Material Compostion
Zn (~95%), Al (~4%), Mg (~0.03-0.06%), Cu (trace), Lower aluminum content, Hardness: 80-100 BHN, Moderate Impact Resistance, Good Wear Resistance, Melting Point: 380-390°C. Lower melting point, energy-efficient, Supperior metal fluidity. More common in thin-walled parts, less poor corrosion resistance, compare to ZA alloys. Cheaper and more widely used in die-casting.
From the above the comparation between both zinc alloys, different zinc alloys can be used in different industrial applications. Depends on the specific demand in various industries, we can select Zamak for high-volume, thin-walled die-cast parts where cost and ease of casting matter, but ZA alloys for stronger, wear-resistant components, especially in bearing and structural applications. This is the difference that zinc-aluminum (ZA) alloys vs. zamak alloys.
Study Case Applications For ZA And Zamak Alloys
Automotive Gearbox Housing -ZA Alloys Die Casting Study Case
Like these zinc alloy die casting components, belongs to medium size zinc die casting parts. Their attribute focus on the specific features of strong corrosion resistance, high strength and easy to cast. Our engineering team can design precise tooling steel die with advanced CAD software. Then well-experienced technician follows the design drawing for the die, and fabricate high precision casting die and finish the turnkey project.

Common ZA Alloys Applications
| ZA Alloy Material | Applications |
|---|---|
| ZA-8 | Easiest to cast for small gears, bushings, low-medium load parts |
| ZA-12 | Automotive components (brackets, pulleys) Industrial machinery parts |
| ZA-27 | Highest strength, hardest to cast, Bearings, sliding parts (replaces bronze in some cases) Heavy-duty industrial applications |
Choose The Right ZA alloy
In order to the specific functional requirement, we select ZA-27, which has lightweight,high strength, strong corrosion resistance and easy to cast. Under the lower temperature, the gearbox housing is made out easily. This ZA features as the follow.
LightWeight
Density ~5.0 g/cm³, lighter than steel/bronze
High Strength
400-440 MPa tensile strength, comparable to cast iron
Lower Melting Points
420-480°C comparison lower melting points, saving more energy consumption.
Resists Oxidation & Corrosion
Better than plain zinc but needs coatings for harsh environments
High Quality Gearbox Housing Mass Production
Firstly, our engineering collaborate with our mold technician fully, design and manufacture high preformance precise tooling steel casting die. and have a trial prototype testing, and remain continuous mold improvement and adjustment until making out satisfied sample. Record the operation parameter and regulate the operation guide.
Secondly, Our production supervior arrange mass production, employers fill the selected zinc ingot into the melting pool, and keep the steady temperature molten metal and ready for casting. Technician set up the parameter of die casting machine well, and start mass production in high efficiency. In order to ensure the smooth surface of the gearbox housing, reduce porosity stats, our technician will take some measures to troubleshoot it.
At last, Triming the flash on the suface of component with cnc machining equipment, and bead shooting the die casting part, and removes the burrs and sharp edges. Sometime they need Plating on the surface of them and enhance their apperance and durability, chrome electroplating for corrosion resistance.

Car Key Case Cover-Zamak Alloys Die Casting Study Case
A professional automotive parts manufacturer needed a cost-effective, high-strength, and corrosion-resistant material for mass-producing car key case covers. These zinc die casting parts must be high dimensional accuracy, Smooth surface finish (for plating/painting), Good wear resistance (to withstand frequent use) and good mechanical properties.

Common Zamak Alloy Applications
| Zamak Items | Applications |
|---|---|
| Zamak 2 | Sporting Goods: high-end fishing reels, industrial components, such as tubing fitting, valves and jigs. |
| Zamak 3 | Casing for razors, lighters, camera bodies, toy cars (e.g., Hot Wheels), zipper sliders.seat belt components, various knobs and levers, decorative trim for automotive industry,furniture hardware, such as hinks, handles and lock mechanism. |
| Zamak 5 | heavy-duty lock components, parts in seat mechanisms, Gears, pulleys, bushings, and other light-duty mechanical parts in industrial equipment. Housing for precision measuring instruments. |
| Zamak 7 | Plumbering fitting, automotive exterior decorative components and consumer electrics buttons. |
Choose The Right Zamak Alloy
After evaluating options between aluminum and ZA alloys, we chose Zamak 3 (Zn-4Al-0.03Mg) for its excellent castability, strength, and flexiable geometries available. It has these features as the below:
High Fluidity
Low melting point (~385°C) ensures smooth filling of thin-walled handle design
Surface Finish
Produces near-net-shape parts with minimal porosity, reducing post-machining
Cost Efficiency
Cheaper than aluminum or ZA alloys for high-volume production
Goog Ductility
The zinc alloy can create the small size intricate die casting part with thin walls.
Die Casting Process
Step 1: Mold Design And Manufacturing
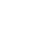
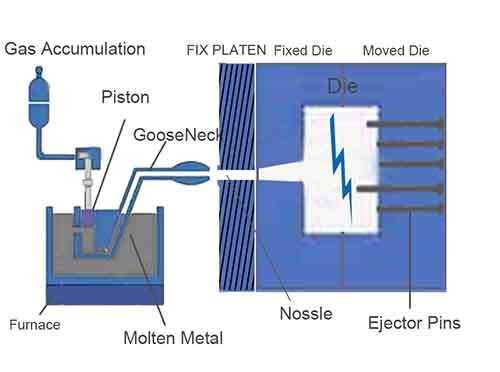
Tool Steel Mold (H13) is selected, our engineers and designers design the precisoin steel casting die with Auto-CAD software. Depends on the principle of hot chamber die casting process, setting cooling channels for rapid solidification. Using EMD machining, process high precision cores and cavities of the casting die, come with appopriate ejection mechanism, finish the mold design and manufacturing.
Step 2: Melting & Casting
Using integrated furnace to melt Zamak 3 ,Melting Temp: ~390°C, maintain the steady temperature zinc alloy molten in melting pool, and preheat the casting die, equal to the temperature of melting zinc alloy. Injecting the molten zinc into the casting die under injection Pressure: ~800-1,200 bar. Then cools the casting die and solidifies the zinc inside the die in a fews seconds. The die is opened, the shaped cast part is ejected out from the die.
Step 3: Post-Processing
Although these zinc alloy die casting parts have a fine surface finish, but the burrs and sharp edges should be trimmed. They accept trimming: Removal of flash via automated trimming. Sometime they need Plating on the surface of them and enhance their apperance and durability, chrome electroplating for corrosion resistance & aesthetics. Conduct Strict Quality Control: X-ray inspection for internal defects.
Conclusion
ZA Alloys vs. Zamak Alloys, Mainly Shown in different sector applications in one industry. Because different composition zinc alloy has different metal properties. Zinc-aluminum alloys have a strong strength mechanical properties, and suitable for precision industrial equipment and automotive parts,but Zamak alloys are common easier to cast, and for electronic consumer goods, hardware, gifts and cloth accessories.